United Kingdom Diploma
Which website can buy Cambridge GCE A-level certificates
- Product ID:United Kingdom Diploma
- QQ:799520747
- WhatsApp: +86 13690285467
- WeChat: 236461877
- Email: diplomacenter@qq.com
- Time: 2024-08-12 17:31
- FEEDBACK
How much does it cost to buy A fake GCE A-level certificate?Which website can buy Cambridge GCE A-level certificates,GCE A-Level certificate Sample,Where can I buy A-Level certificates,What is an GCE A-level certificate?

(2012 GCE A-level Certificate)

(2012 GCE A-level Certificates)
The A-level (Advanced Level) is a subject-based qualification conferred as part of the General Certificate of Education, as well as a school leaving qualification offered by the educational bodies in the United Kingdom and the educational authorities of British Crown dependencies to students completing secondary or pre-university education,They were introduced in England and Wales in 1951 to replace the Higher School Certificate. The A-level permits students to have potential access to a chosen university they applied to with UCAS points. They could be accepted into it should they meet the requirements of the university.
-
Subjects: Students usually choose three or four subjects to study in-depth. These subjects can range from Mathematics and Sciences to Humanities and Arts.
-
Exams: The A-level qualification is usually obtained through a series of exams, often taken at the end of a two-year course (though some subjects might be assessed through coursework as well).
-
Grades: The results are graded from A* (the highest) to E (the lowest), with U indicating ungraded. The grades are used for university admissions and can also influence job prospects.
-
Purpose: A-levels are primarily used for university entry in the UK. They are recognized internationally and can be a requirement for certain higher education courses and professions.
-
Structure: The A-level program is divided into two parts: AS-levels (Advanced Subsidiary) and A2-levels. AS-levels are taken in the first year and A2-levels in the second year. Combined, they form the full A-level qualification.

(2015 GCE A-level Certificate)
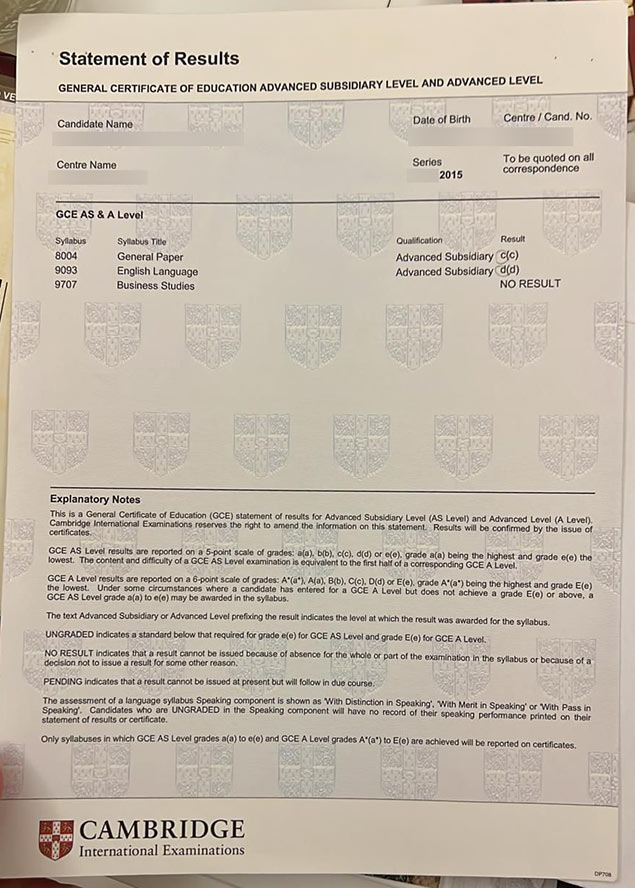
(2015 GCE A-level Certificates)
What is the highest grade in GCE A level?A*(a*)GCE Advanced Level - grades A*(a*), A(a), B(b), C(c), D(d), or E(e) indicate a pass at Advanced Level, grade A*(a*) being the highest and grade E(e) the lowest. GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level - grades a(a), b(b), c(c), d(d), or e(e) indicate the standard reached, grade a (a) being the highest and grade e (e) the lowest.
What is an A level equivalent to?Level 3 BTEC National qualifications are considered equivalent to A levels, while Level 2 BTEC Nationals are equivalent to GCSE. The three different BTEC National Level 3 courses available are: Foundation Diploma. Diploma.What is a level certificate in UK?Advanced level qualifications (known as A levels) are subject-based qualifications that can lead to university, further study, training, or work. You can normally study three or more A levels over two years. They're usually assessed by a series of examinations.What is the A level equivalent to in the US?In terms of academic equivalencies, the GCE “A” Level is generally considered to be equivalent to the US Advanced Placement (AP) program or the International Baccalaureate (IB) program.GCE a level grading system?The pass grades for A Levels are, from highest to lowest, A*, A, B, C, D and E. Those who do not reach the minimum standard required for a grade E receive the non-grade U (unclassified), and those who fail to complete any of the subject's components will receive an X. There is no A* grade at AS level.

(2016 GCE A-level Certificate)
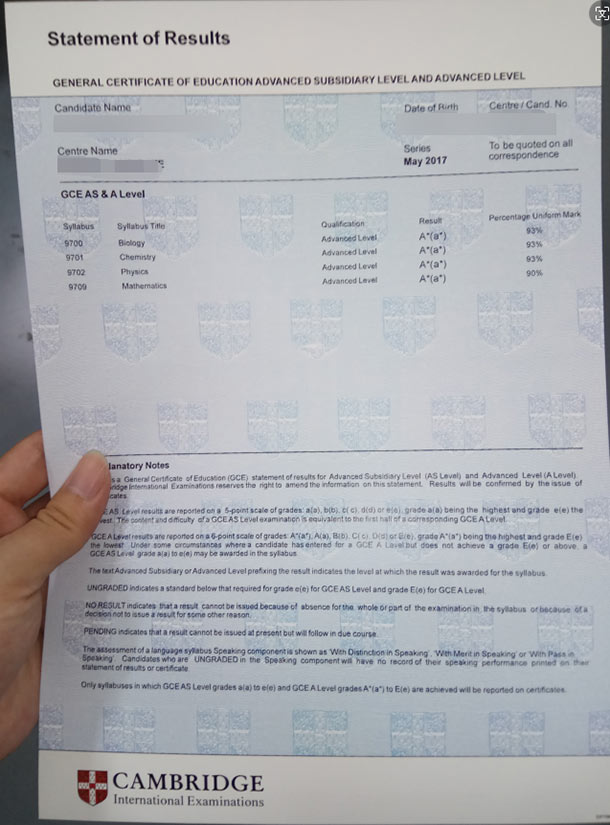
(2017 GCE A-level Certificate)
What is the difference between A level and GCSE?
A-levels and GCSEs are both key qualifications in the UK education system, but they serve different purposes and are designed for different stages of education.
Stage of Education:
-
GCSEs (General Certificate of Secondary Education):
- Age Group: Typically taken by students aged 14-16 (Years 10 and 11).
- Purpose: Marks the end of compulsory education. GCSEs provide a broad foundation of education and are often required for entry into further education or training.
-
A-levels (Advanced Levels):
- Age Group: Typically taken by students aged 16-18 (Years 12 and 13).
- Purpose: Used primarily for university entry and to specialize in a smaller range of subjects in greater depth. A-levels are more advanced and build on the knowledge and skills gained at GCSE level.
2. Curriculum and Specialization:
-
GCSEs:
- Subjects: Students usually take a range of subjects, including core subjects like English, Mathematics, and Science, along with additional subjects chosen from a broad selection (e.g., History, Geography, Art).
- Focus: Provides a general education and covers a broad curriculum.
-
A-levels:
- Subjects: Students typically choose three to four subjects to study in-depth. They may specialize in areas such as Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, History, etc.
- Focus: Allows students to focus intensively on a few subjects, preparing them for higher education or specific career paths.

(2020 GCE A-level Certificate)3. Assessment:
-
GCSEs:
- Assessment: Generally assessed through a combination of exams and coursework. Exams are usually taken at the end of Year 11.
- Grading: Graded from 9 to 1 (with 9 being the highest), replacing the old A* to G grading system.
-
A-levels:
- Assessment: Primarily assessed through final exams at the end of the two-year course, though some subjects may include coursework or practical assessments.
- Grading: Graded from A* to E, with A* being the highest.
4. Purpose and Progression:
-
GCSEs:
- Purpose: Provide a broad educational foundation and are often required for further education options such as A-levels, vocational courses, or apprenticeships.
- Progression: Essential for moving on to post-16 education options.
-
A-levels:
- Purpose: Specialize in specific subjects and are mainly used for university admissions or other advanced educational and career opportunities.
- Progression: Serve as a key qualification for higher education and are important for university and career pathways.

(2022 GCE A-level Certificate) -
Recommended reading:What's the GCE certificate-Buy GCE fake Certificate Onilne
CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
Wechat: 236461877
WhatsApp: +86 13690285467
Email: diplomacenter@qq.com



